How to track Bitcoin transaction
Bitcoin is a digital asset infrastructure powering the first worldwide decentralized cryptocurrency of the same name. All Bitcoins’ addresses and transactions are available through a public ledger called a blockchain. Through blockchain analysis, transactions and addresses can be easily analysed. However, identifying the owners of addresses is another story, as this data is not provided anywhere. This is why Bitcoin is termed pseudo-anonymous. Let’s dive into how to track a Bitcoin transaction and Bitcoin address.
Track a Bitcoin Transaction
According to Bitcoin:
“All Bitcoin transactions are public, traceable, and permanently stored in the Bitcoin network.”
Let’s start by what means are publicly available to track a Bitcoin transaction. Blockchain analysis is possible because nearly all cryptocurrencies are recorded on permanent blockchains that act as ledgers, making data publicly available. Blockchains store data on transactions through which you can see the amount that is moved between cryptocurrency addresses, which are pseudonymous by default. However, blockchain analysis tools only record the movements of cryptocurrency between discrete addresses, as recorded on blockchains themselves.
This means that tracking Bitcoins gets more complicated when someone sends cryptocurrency to an address hosted at a service like an exchange, even if you know the specific deposit address associated with an individual user. When someone sends cryptocurrency to their deposit address at an exchange service, the cryptocurrency doesn’t just sit at that address. Instead, the service moves the funds around internally and mingles them with the funds of other users.
Because blockchains don’t understand that these internal fund movements are not ordinary transactions, they are recorded in the ledge like any other transaction. Therefore, there is no use to keep following funds on the blockchain, as soon as they are deposited to a service. The owner of the deposit address is not the one moving the funds around at that point, but the exchange service does. Only the exchange service knows what transactions are associated with which users, and this information is not visible on blockchains.
But more on this later. First, let’s see how to trace ordinary Bitcoin transactions.
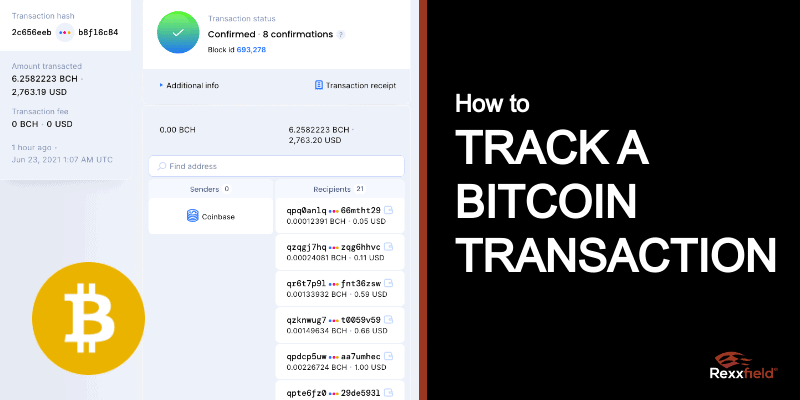
Bitcoin transaction lookup
There are plenty of Bitcoin transaction lookup tools available that can provide useful data.
A Bitcoin transaction ID looks like this: 2c656eebab2b267012a9a9a5976375aaf4d72970c28177498c6bac2cb8f16c84
Blockchair – Blockchair stores data from 17 blockchains. You can search for transactions, addresses, blocks, and embedded text data.
Blockchain Explorer – The Blockchain Explorer provides data for Bitcoin, including historical prices, the most recently mined blocks, the mempool size of unconfirmed transactions, and data for the latest transactions.
BTC.com – Here you can search data via an address, height, or block hash.
Bitcoin Block Explorer – Provides data based on transactions, addresses, and a block hash.
Tracking a Bitcoin address
Tracking a Bitcoin address is easy since there is address data readily available. A Bitcoin address is a series of letters and numbers unique to its wallet, and the publicly available information for tracking a Bitcoin address includes:
- Wallet balance
- Transactions information, such as:
- Amount of cryptocurrency sent
- Sender’s Bitcoin address
- Receiver’s Bitcoin address
- Date of transfer
- Associated charged fees
- # of confirmations on the transaction
However, the identity of the Bitcoin address’s owner is not provided. Identifying the owner is complicated, but not impossible.
Check a bitcoin wallet
To check a Bitcoin wallet balance, enter the Bitcoin address in Cointracker to see the wallet balance on the blockchain.
Example of how scammers launder stolen Bitcoin funds
As we established, tracking a Bitcoin transaction is easy. However, tracking Bitcoin transactions gets more complicated when funds are sent to addresses that are hosted on an exchange, and they get moved and mingled around with other funds and users. Scammers launder their funds by sending them through Bitcoin mixing services. These mixing services make it very challenging to follow the money trail any further, to find out where these funds are spent or cashed out.
The 2020 Twitter Hack Bitcoin Money Laundering Scam Example
Elliptic showcased the 2020 Twitter, and Hack Bitcoin Money Laundering Scam. The graphs so how the bitcoins were distributed through different wallets, using different addresses.
Timeline:
- From three original addresses, the scammers divided the bitcoins into numerous other bitcoin wallets. Almost all of the funds were sent to 12 new addresses. Only a very small proportion of the funds were sent to known, regulated crypto exchanges through which law enforcement would be able to ask the exchanges to release the identity of the account holder who received these funds.
- Then, 22% of the stolen funds were sent to an address that is believed to have been part of a Wasabi Wallet. Wasabi Wallet is a type of bitcoin wallet that can hide transaction trails, making it challenging for law enforcement, private investigators, and financial institutions to track Bitcoin transactions on the blockchain.
- Within 24 hours, the scammers used mixers to split the funds into smaller amounts through numerous transactions. But by this time, the majority of the funds were spent or cashed out through an exchange service. By splitting the remaining funds in smaller amounts, and distributing them to numerous wallets, using several addresses, scammers were buying time to work out how to cash out without being identified, as their movements were being tracked on the blockchain.
- In the following days, the Bitcoin scammers continued to split the stolen funds into ever-smaller amounts and passed it through mixers and unregulated exchanges.
Mixing services, and using exchange services, make it challenging, if not impossible, to follow the blockchain money trail any further. In many, but not all, cases this stops the money trail and funds are lost.
But there is another strategy to recover stolen funds, by identifying the owner through obtaining an IP address.