Cryptocurrency trading is when two individuals or groups exchange their digital assets. They buy and sell off digital assets like Etherium, Bitcoin etc. Unfortunately, there are many scammers preying for victims to deceive into trading or investing cryptocurrency to end up stealing their assets. These are cryptocurrency trading scams.
Cryptocurrency trading scams usually target individuals in an effort to get sensitive information, such as security codes, to lure their victims into transferring their digital crypto assets to a compromised digital wallet.
The various types of scams include fraudulent mining applications, extortion emails, giveaways, phishing, romance schemes, blackmail, and “rug pulls”.
If you are a victim of a cryptocurrency trading scam, watch out for recovery scammers.
Types of Cryptocurrency Trading Scams
There are two major cryptocurrency trading scams:
- Difi Wallet Scam: this is the creation of a fake wallet application by crypto scammers to lure individuals into depositing their crypto asset. They create phishing links, buy or build a social media account with huge followers and ads to promote their fake apps. Once you click the phishing link, you innocently give the scammers access to your digital assets without realizing it and your personal information too. This makes your funds vulnerable to theft or fraud.
- Crypto ponzi scheme: designed to lure victims into the promise of high or steady returns that are a cut above the market norm. The scheme misleads investors into believing that profits originate from lawful business operations, when in reality it is a hoax. The scheme’s apparent success stems from a continuous inflow of new investors’ money to pay out earlier investors and to keep the operation going. There are other schemes that involve transfer of funds directly to crypto bandits through imposture, fake business opportunities or other deceiving means.
How They Work
Psychological Manipulation
This is mostly the use of social engineering scams; the scammers condition their victims to think they are communicating with trusted structures like tech support, a friend, government body, a colleague, or a popular business.
Fraudsters will invest significant time in winning the trust of a potential victim before soliciting the individual to disclose private keys or transfer funds to their digital wallet. Any request for cryptocurrency from a supposedly credible source should be regarded as a red flag for potential fraudulent activity.
Romance Scam:
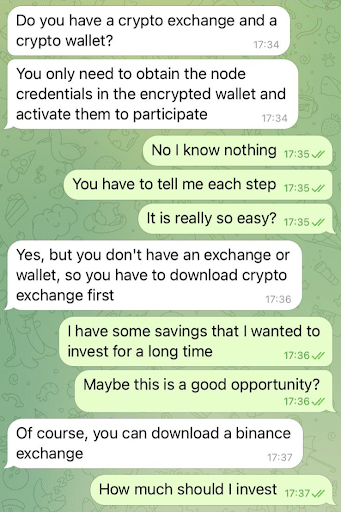
It came to the notice of the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in 2022 that cryptocurrency accounted for close to 20% of the reported monetary losses in romance scams. The FTC also determined that the schemes related to romance scam are the most common type of financial scams with a total of $1.3 billion stolen.
Imposter and Giveaway Scam:
This is another orchestrated plot by scammers to steal your funds. Impersonation and fraudulent giveaways, are designed to portray themselves as public figures offering false promises of multiplying or matching cryptocurrency transfers.
They skillfully construct communication from what appears to be a genuine social media account to generate a feeling of legitimacy and immediacy. This illusion of a unique investment opportunity may entice individuals to transfer funds expecting immediate gains. Fraudsters posing as members of the cryptocurrency exchange’s support or security teams also reach out to deceive owners of cryptocurrency into relinquishing their funds.
Blackmail and Extortion Schemes:
Blackmail is another scheme these scammers use. They may gain or pretend to possess illicit material of potential victims and threaten to disclose this information unless the victims reveal their private keys or cryptocurrency. Issues like this are termed as criminal extortion and should be promptly reported to law enforcement authorities, such as the FBI or contact us for swift action.
Phishing Cryptocurrency Scam:
This is designed to obtain the private keys of individuals. These keys are essential for accessing and securing cryptocurrency within software wallets.
Cloud Mining
The use of rented cloud computing power, without installing and directly running the hardware and related software in a mechanized way is called cloud mining. Here, developers market to retail buyers and investors. The goal is to make them contribute their funds, to secure a continuous supply of mining power and rewards.
Cloud mining platforms target retail investors and buyers in order to secure initial capital for a continuous supply of mining power and rewards. These platforms often lack ownership of the hash rate they claim and fail to deliver rewards after receiving the initial payment. While cloud mining itself may not be fraudulent, it is important to conduct thorough due diligence on the platform before making any investments in order to protect your capital.
Rug Pulls
Here, developers abruptly and deliberately withdraw all liquidity to a project they once hyped to become the next big thing in the crypto realm once they have raised funds or cryptocurrency from their victims’ investment. They eventually run off with all the money leaving their investors with nothing.
NFTs and ICOs
While NFTs focus on uniqueness and ownership, ICOs focus on raising funds by selling tokens for startups giving the room to scam individuals. They usually don’t tally with the standard market conditions, so it is important to have a good judgment when considering the potential gains of crypto based investment to avoid stories that hurt.
How To Recognize Cryptocurrency Trading Scams
- Ignore calls, emails and text messages from well known or unknown companies or organizations saying that your account is frozen and they want to help you to unfreeze it.
- No celebrity will contact you about buying a cryptocurrency.
- Reach out to your regulatory agency if you receive a call, an email or text message from any governmental body or company stating that your assets are frozen. Always connect with the agency’s official website if that is the case.
- Avoid job listings for cash to crypto converter or crypto miner openings.
- Examine claims about detailed materials that scammers may say they have about you that they threaten to post if you don’t send cryptocurrency. Don’t pay them. If you pay them once, they will continue to blackmail you. Report it.
- Never give out your private keys to anyone. Those keys prevent unwanted access to your crypto wallet and no one needs them for legitimate cryptocurrency transactions.
- Don’t give out funds to random strangers claiming to love you on dating sites, meet them in person if their claims are genuine.
- Don’t accept FREE funds.
- Ignore investment managers that contact you promising quick returns.
How To Avoid Getting Scammed When Dealing With Cryptocurrency Trading?

It is important for white papers to prominently feature the individuals and developers associated with the cryptocurrency. In some instances, open-source crypto projects may not explicitly list developers, a common practice within open-source environments. However, documentation such as coding, comments, and discussions can usually be found on platforms like GitHub or GitLab. Additionally, some projects use forums and communication applications like Discord for community discussions. If these elements are not available and the white paper contains numerous errors, we advise you to be careful, as it may be indicative of potential cryptocurrency trading scams.
Explore The Market Structure
Whoever told you that Investing in cryptocurrencies is a typical means of generating profit lied. They feature coins or tokens to facilitate the function of the blockchain. True cryptocurrency projects will not promote itself on social media or hype itself about being the next big thing. Updates related to cryptocurrencies mostly focus on advancements in blockchain technology or enhanced security measures; they won’t emphasize on fundraising successes.
Read The White paper
Cryptocurrencies undergo a structured developmental phase, which typically includes the release of a publicly-available document known as a white paper. A legitimate white paper will provide comprehensive descriptions of the protocols and blockchain, as well as detailed explanations of formulas and the overall network functionality.
Counterfeit cryptocurrencies fail to provide comprehensively crafted and thoroughly researched white papers. The fraudulent documents are inadequately written, containing inconsistent figures, and lack detailed explanations of the projected utilization of the funds raised.
It is recommended to review the white papers of reputable cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum and Bitcoin, for comparison. It is important for white papers to feature the individuals and teams responsible for the development of the cryptocurrency. In some instances, most times, those cryptos with open-source projects do not have specific developers, which is the standard for open-source projects. Typically coding can be found in, discussion and comments, on GitLab or GitHub. Additionally, some projects utilize forums and platforms like Discord for communication. If these elements are not present and the white paper contains numerous errors, it is advisable to refrain from further engagement, as it may indicate a fraudulent scheme.
Beware of Air drops
Several cryptocurrency scams entice individuals with free coins or the promise of receiving coins directly into their wallets. It is essential to bear in mind that nothing is truly free, especially in the realms of finance and cryptocurrencies.
How to Report Cryptocurrency Trading Scams
If you are the victim of cryptocurrency trading scams, inform the authorities either by contacting the police or your country’s designated fraud reporting platform. For example:
- Nigeria – www.efcc.gov.ng/efcc/,
- United States of America – www.ic3.gov,
- United Kingdom – www.actionfraud.police.uk ,
- Canada – www.antifraudcentre.ca,
- Australia – www.cyber.gov.au.
It is recommended to notify both your financial institution and tax authority about any instances of cryptocurrency trading fraud or deception.
In recent years, law enforcement agencies have come to acknowledge the importance of public-private partnerships in successful crypto scam recovery operations. Due to overwhelming caseloads, not all cases can be immediately addressed, resulting in delays for victims seeking assistance. This wait time increases the complexity to recover scammed cryptocurrency, as officers are already managing workloads typically meant for more than 20 agents.
We investigate scams, locate stolen assets, and scammers, and provide our all findings to law enforcement to increase the chances of law enforcement to take our client’s cases.
What are the common cryptocurrency trading scams
They include romance and phishing scams, investment schemes and rug pulls.
Can one get scammed if someone sends them crypto?
Absolutely! Do not accept transactions from any organization or persons you are not familiar with, especially where they ask you to disclose your private keys to run a smooth transfer or they send you a link to paste in your wallet claiming that such action will run a smooth transfer of funds to your wallet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cryptocurrency trading scams are a real risk in the digital currency space. By staying informed, conducting due diligence, and exercising caution, individuals can reduce their likelihood of falling victim to these scams. Additionally, being aware of the common types of cryptocurrency trading scams and following best practices for protecting oneself can help mitigate the risk of financial losses and fraud. If you encounter a potential scam, it’s essential to take immediate action to protect yourself and prevent further harm.
If you need our crypto forensics to investigate your case, please get in touch.
Contact our crypto investigators
Author contribution: Hãmsár


